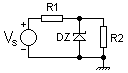
Zener regulator
where, VZ is the Zener voltage, and IR2 is the required load current.
This regulator is used for low power applications very easily where currents involved are very small and the load remains connected across the Zener diode (such as voltage or reference voltage source circuit). After R1 has been calculated, remove R2 will cause full load current (plus the zener current) flows through the diode and can exceed the maximum current rating of the diode ruin. Regulation circuit also not as good as the zener current (and thus the zener voltage) will vary depending on the VS and inversely dependent on the load current.
Voltage series regulator
Adding an emitter-follower stage to easily form a zener regulator voltage regulator series is easy and significantly improves the control circuit. Here, IR2 load current supplied by transistor whose base is now connected to the Zener diode. Thus the transistor base current (IB) form the load current and the Zener diode is much smaller than the current through R2. Regulator is classified as a "series" for regulating element, namely, transistors, appearing in series with the load. R1 set the Zener current (IZ) and determined to be -
where, VZ is the zener voltage, the transistor base current IB is K = 1.2 to 2 (to make sure that R1 is low enough for adequate IB).



No comments:
Post a Comment